【入門】TensorFlow ProbabilityによるMCMC

本記事では、TensorFlow Probabilityを用いたMCMCの実装を解説します。
TensorFlow Probabilityとは
TensorFlow Probabilityは、TensorFlowを用いて確率推論や統計分析を行うライブラリです。
Distribution Classの使い方
まずは、高度な確率推論を行う前に確率分布を扱うための便利なdistributionクラスについて学ぶ必要があります。
基本的にdistributionクラスのオブジェクトは、設定した確率分布に従うサンプルを生成するsampleメソッドとある入力値の対数の確率分布を計算するlog_probという二つのメソッドを使用することができます。
単変量確率分布の具体例
まずは、単変量ガウス分布の具体例を以下に示します。
# 標準正規分布の具体例
# Distribution Objectを作成
normal = tfd.Normal(loc=0., scale=1.)
# sampling
samples = normal.sample(1000)
sns.distplot(samples)
plt.title("標準正規分布に従うサンプル")
plt.show()
# log prob
print("対数の確率密度 (一点)", normal.log_prob(0.))
print("対数の確率密度 (複数点)", normal.log_prob([-1., 0., 1.]))
<output>
対数の確率密度 (一点) tf.Tensor(-0.9189385, shape=(), dtype=float32)
対数の確率密度 (複数点) tf.Tensor([-1.4189385 -0.9189385 -1.4189385], shape=(3,), dtype=float32) 
多変量確率分布の具体例
次に多変量正規分布の具体例を以下に示します。
# 多変量正規分布の具体例
# Distribution Objectを作成
mvn = tfd.MultivariateNormalDiag(loc=[0., 0.], scale_diag = [1., 1.])
# log prob
print("対数の確率密度 (一点)", mvn.log_prob([0., 0.]))
print("対数の確率密度 (複数点)", mvn.log_prob([[0., 0.], [1., 1.]]))
# sampling
samples = mvn.sample(3000)
print("生成されたサンプルの形状", samples.shape)
sns.jointplot(x=samples[:, 0], y=samples[:, 1])
plt.show()
<output>
対数の確率密度 (一点) tf.Tensor(-1.837877, shape=(), dtype=float32)
対数の確率密度 (複数点) tf.Tensor([-1.837877 -2.837877], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
生成されたサンプルの形状 (3000, 2)
batch属性とevent属性
Distributionsクラスでは、同じ確率分布でパラメータの異なる分布を同時に扱うことができます。その分布の数をbatch_shapeと呼び、確率分布の次元のことをevent_shapeと呼びます。
具体例を見た方がわかりやすいと思うので、具体例を以下に示します。
# shape (batch : 同じ分布族に属する確率分布の数, event : 次元)
normals = tfd.Normal([-1.0, 1.0], [0.5, 1.5])
print("Batch shape:", normals.batch_shape)
print("Event shape:", normals.event_shape)
print("batchごとの対数確率分布", normals.log_prob([-1.0, 1.0]))
xs = np.linspace(-6, 6, 200)[..., np.newaxis]
samples = normals.sample(1000)
print("生成されたサンプルの形状", samples.shape)
for i in range(2):
sns.distplot(samples[:, i], kde=False, norm_hist=True)
plt.plot(np.tile(xs, 2), normals.prob(xs), c='k', alpha=.5)
plt.title("二つの正規分布に従うサンプル")
plt.show()
<output>
Batch shape: (2,)
Event shape: ()
batchごとの対数確率分布 tf.Tensor([-0.22579134 -1.3244036 ], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
生成されたサンプルの形状 (1000, 2)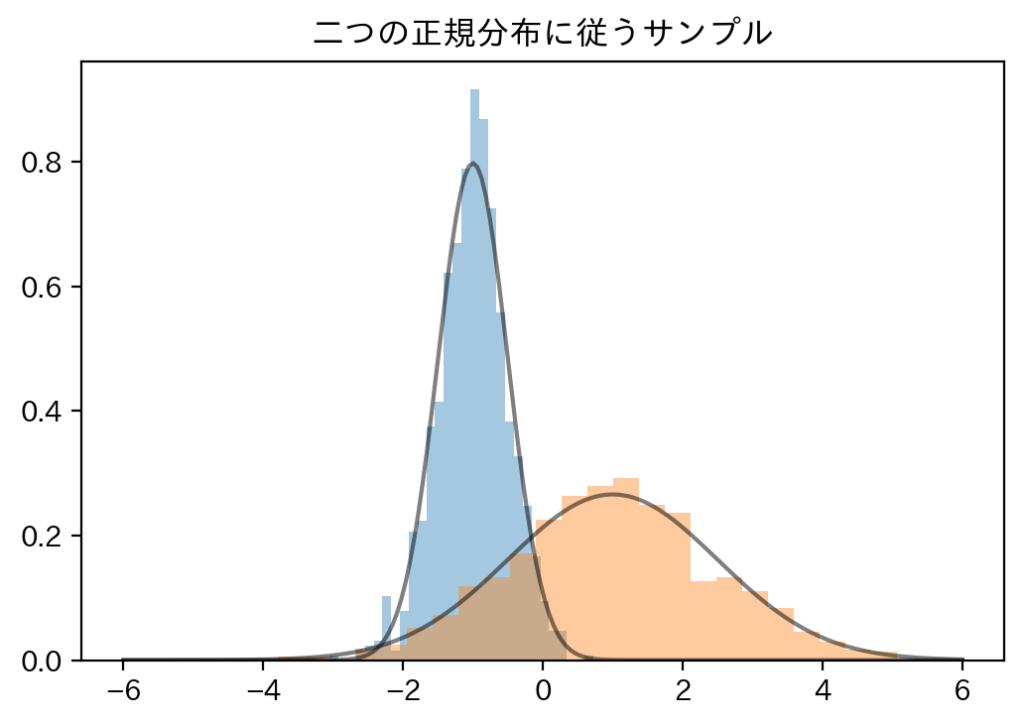
TensorFlow ProbabilityによるMCMC
ここからは、TensorFlow Probabilityを用いた基本的なMCMCの実装を紹介します。
基本的には、以下の手順でMCMCを実装することができます。
- 規格化されていない対数の確率分布を定義(エネルギー関数)
- 遷移方法を定義(kernelを設定)
- MCMCを実行(
tfp.mcmc.sample_chain)
まずは、最も簡単な標準正規分布のコード例を最初に紹介します。
① : 規格化されていない対数の確率分布を定義(エネルギーを定義)
まずは、規格化されていない対数の確率分布を定義しましょう。
# 規格化定数を除く対数の確率分布を定義
def unnormalized_log_prob(x):
return - 0.5*(x**2.)
② : 遷移方法を定義(kernelを設定)
次に遷移方法を設定しましょう。
今回は、簡単のためRandomWalkを用いたMetropolisを設定します。
# kernelを設定
kernel = tfp.mcmc.RandomWalkMetropolis(
target_log_prob_fn=unnormalized_log_prob)
③ : MCMCを実行
MCMCを実行するためには、tfp.mcmc.sample_chainを使用します。
具体例を以下に示します。
# MCMCを実行
samples = tfp.mcmc.sample_chain(
num_results=10000,
current_state=1.,
kernel=kernel,
num_burnin_steps=500,
trace_fn=None,
seed=42)
sample_mean = tf.math.reduce_mean(samples, axis=0)
sample_std = tf.sqrt(tf.math.reduce_mean(
tf.math.squared_difference(samples, sample_mean),
axis=0))
print(f'平均の推定値 {sample_mean:.3f}')
print(f'標準偏差の推定値 {sample_std:.3f}')
sns.distplot(samples[::5])
plt.show()
<output>
print(f'平均の推定値 {sample_mean:.3f}')
print(f'標準偏差の推定値 {sample_std:.3f}')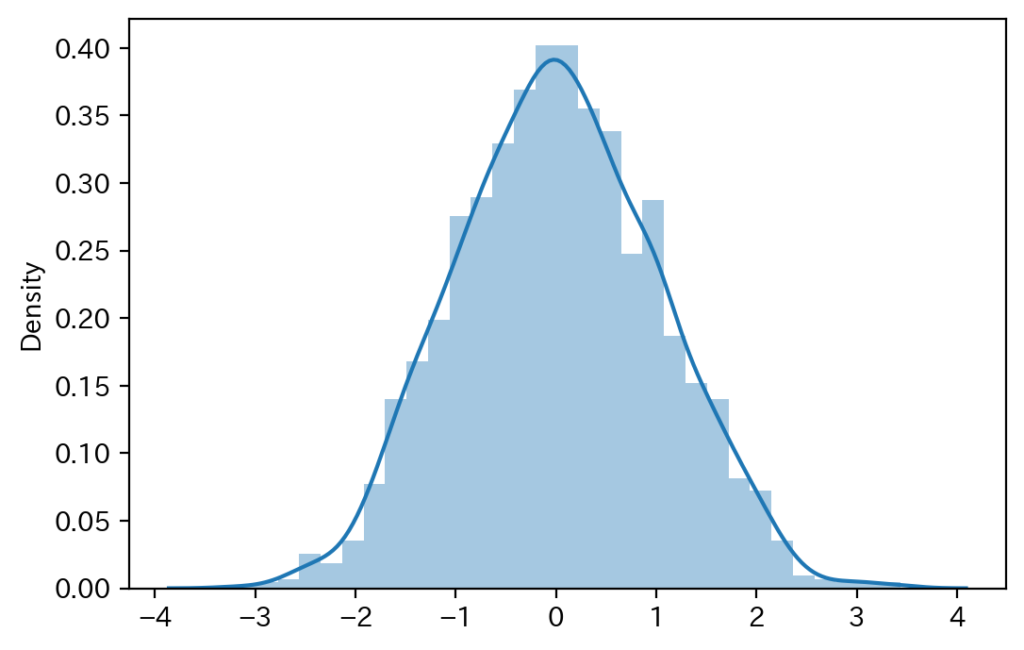
無事、正規分布からサンプルが生成できました。
一応、二次元正規分布の具体例も紹介しておきます。
# 規格化定数を除く対数の確率分布を定義
def unnormalized_log_prob(x):
return - 0.5*(x**2.)
# kernelを設定
kernel = tfp.mcmc.RandomWalkMetropolis(
target_log_prob_fn=unnormalized_log_prob)
# MCMCを実行
samples = tfp.mcmc.sample_chain(
num_results=10000,
current_state=np.ones(2, dtype=np.float32),
kernel=kernel,
num_burnin_steps=500,
trace_fn=None,
seed=42)
sample_mean = tf.math.reduce_mean(samples, axis=0)
sample_std = tf.sqrt(tf.math.reduce_mean(
tf.math.squared_difference(samples, sample_mean),
axis=0))
print(f'平均の推定値, {sample_mean[0]:.3f}, {sample_mean[1]:.3f}')
print(f'標準偏差の推定値, {sample_std[0]:.3f}, {sample_std[1]:.3f}')
sns.jointplot(x=samples[::5, 0], y=samples[::5, 1])
plt.show()
<output>
平均の推定値, -0.047, 0.014
標準偏差の推定値, 1.029, 0.992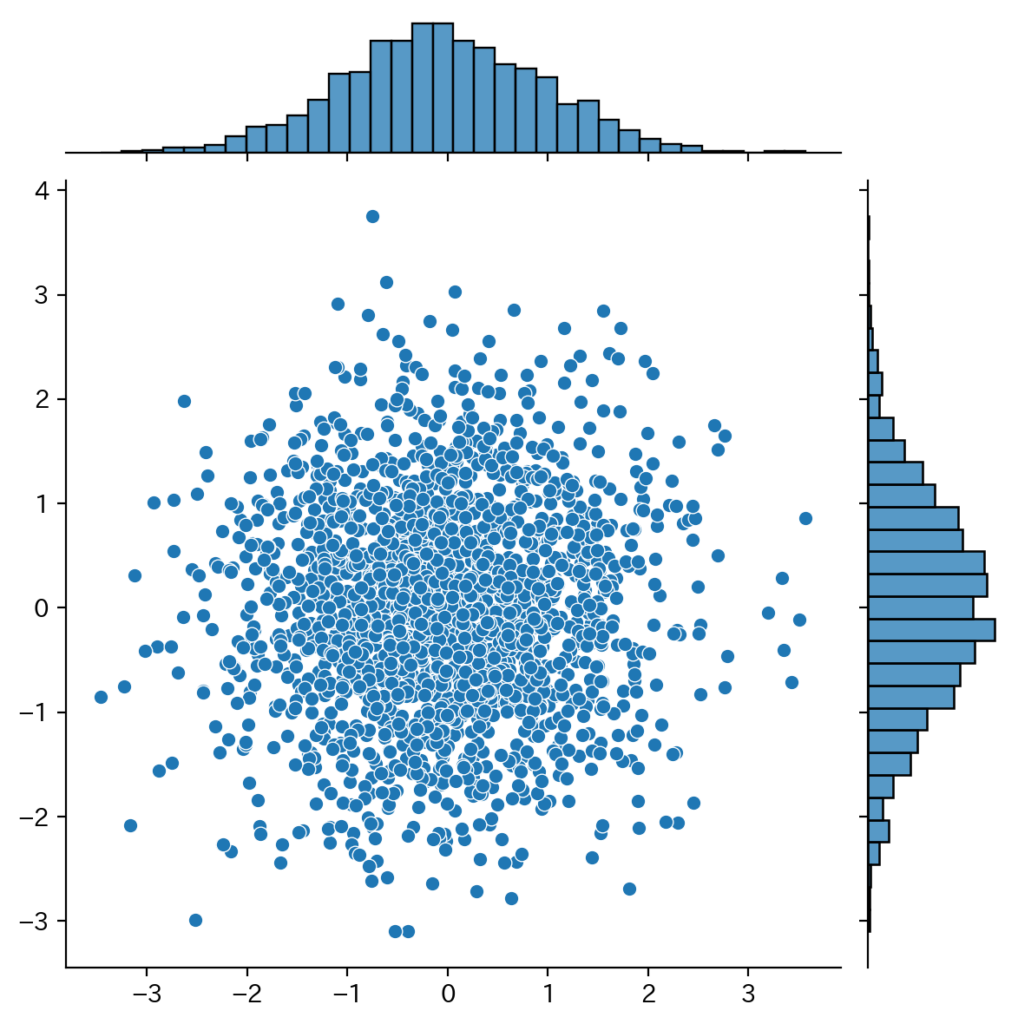
まとめ
本記事では、TensorFlow Probabilityを用いてMCMCを実装する方法を簡単に説明しました。
スクラッチでMCMCを実装するよりもかなり簡単に実装できるのでおすすめです。

Pythonを学習するのに効率的なサービスを紹介していきます。
まず最初におすすめするのは、Udemyです。
Udemyは、Pythonに特化した授業がたくさんあり、どの授業も良質です。
また、セール中は1500円定義で利用することができ、コスパも最強です。
下記の記事では、実際に私が15個以上の講義を受講して特におすすめだった講義を紹介しています。

他のPythonに特化したオンライン・オフラインスクールも下記の記事でまとめています。

自分の学習スタイルに合わせて最適なものを選びましょう。
また、私がPythonを学ぶ際に使用した本を全て暴露しているので参考にしてください。